The amino acid sequence from N- to C-terminus determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. Resonance and peptide bonds.

Peptide Bond Definition Structure Mechanism And Examples
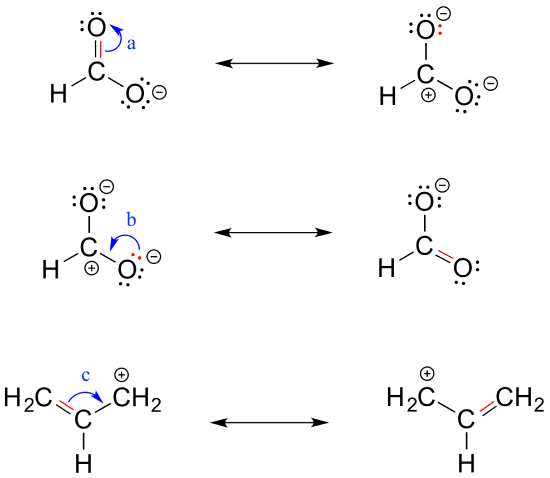
The resonance structure is a significant factor in depicting the true electron distribution.
. In baking the carbon dioxide that is released causes bread to rise and. Structures of the peptide bond below the peptide. Draw the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids.
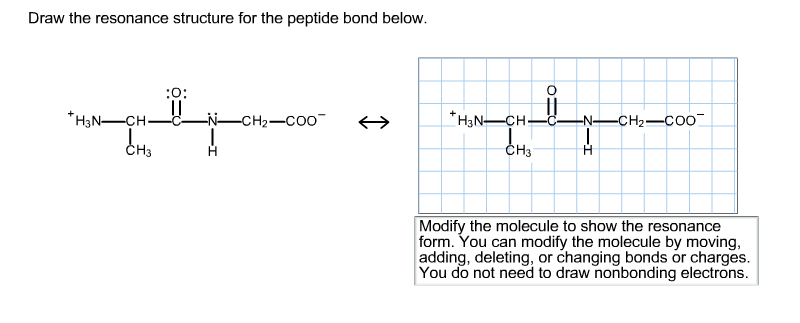
1 When you see two different resonance contributors you are not seeing a chemical reaction. The resonance structure prevents rotation around the peptide bond. Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below.
You do not need to draw nonbonding electrons. Carbonate ion is a common polyatomic ion found in limestone baking powder and baking soda. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide bonds.
The dipole momentof each peptide bond is shown in Figure 1-8. Draw a dipeptide of two amino acids in trans linkage side-chains can be shown as and indicate which six atoms are part of the planar structure of the peptide. Structures of the peptide bond.
In this article we will know about n3- lewis structure resonance molecular geometry formal charge structure angle and hybridization. Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen. Rather you are seeing the exact same molecule or ion depicted in two different ways.
The peptide bond has approximately 40 double-bond character. 1 Pauling and Corey showed that in small peptides six atoms associated with the peptide bond all lie in a plane. The coplanarity of the peptide bond denotes the resonance or partial sharing of two pairs of electrons between the amide nitrogen and carboxyl oxygen.
Draw the condensation reaction resulting in a dipeptide use R1 and R2 as the side chain R groups and. The four atoms that are part of the peptide bond are shown as larger spacefilling models. Resonance constrains the peptide bond so that it CANNOT rotate which gives the polypeptide sequences a backbone.
First it increases the polarity of the peptide bond. Only three nitrogen atoms make up the azoide ion N3. Resonance Structures of Carbonate CO 32 Ion.
Addition of acid to the carbonate ion causes the formation of carbonic acid which decomposes rapidly into water and carbon dioxide. The amino acids are taken from the crystal structure of hemoglobin αVal 132 and αSer 133. The structure at the right shows a peptide bond between the amino acids valine Val and serine Ser.
Below the peptide drawing we redraw this resonance structure and also draw the second resonance structure to show that peptide bonds have double-bond character. The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures. Charges result in the peptide bond having a permanent dipole.
Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen. The C-N distance in a peptide bond is typically 132 Å which is intermediate between the values expected for a C-N single bond 149 Å and a CN double bond 127 Å. The resonance structure prevents rotation around the peptide bond.
Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen. The atoms C H N O of the peptide bond lies in the same plane like the hydrogen atom of the amide group and the oxygen atom of the carboxyl group are trans to each other. The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures.
The stability of the peptide bond as well as other properties important for the behavior of polypeptides is due to resonance the delocalization of electrons over several atoms. Modify the molecule to show the resonance form. The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures.
A Peptide bond b N-terminus c C-terminus d An α-amino group and an ε-amino group e An α-carboxylate group and a Y-carboxylate group Draw the structure of the dipeptide Lys-Glu at pH 70. What is the hybridization state of the nitrogen atom in an amide. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond.
Two NN bonds are present in the Lewis structure of the N3 ion. As a result it is rigid. Overview of protein structure Page.
Chapter 4 The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins 47 40. 24 is asking us to draw the resident structures of the peptide bond so we can start by trying are a peptide bond. The amide structure has two resonance contributors.
2 Resonance contributors involve the imaginary movement of pi-bonded electrons or of lone-pair electrons that are adjacent to ie. You can modify the molecule by moving adding deleting or changing bonds or charges. And then to get the residents structure we can move the electrons from this double bond up to the oxygen that we can move this lone pair from nation between the carbon and nitrogen.
The formation of a peptide bond is what type of reaction. The result is a planar structure that is stabilized by resonance between the α-carboxyl and α-amino groups. Outside nitrogen atoms contain two lone pairs whereas the core nitrogen atom has none.
The resonance structure prevents rotation around the peptide bond. Click on the structure below to switch the resonance forms of the peptide bond. Quizlet is a lightning fast way to learn vocabulary.
After peptide bond formation the first step of translocation is a movement of the 3 ends of the tRNA from A to P and P to E sites of the 50S subunit independent of the stationary anticodon ends. Chemistry questions and answers. This peptide bond structure lecture explains the peptide bond formation and rotation of angles.
Rules for drawing resonance structures. Resonance has two other important consequences. Thus the peptide unit is a planar rigid structure and rotation in the peptide backbone is restricted to the bonds involving the a carbon.
At first glance it would seem logical to say that it is sp 3-hybridized because like the nitrogen in an amine the Lewis structure shows three single bonds and a lone pairThe picture looks quite different though if we consider another resonance contributor in which the. Protein phosphorylation is an example of what. Because the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen has a partial double bond character rotation around this bond is restricted.
The side chains.

Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com
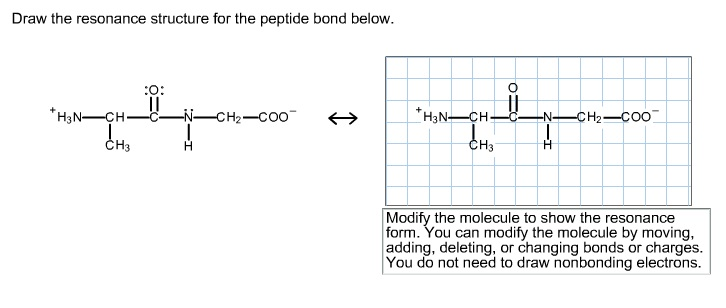
Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com
Peptide Bonds Biochemistry Flashcards Draw It To Know It
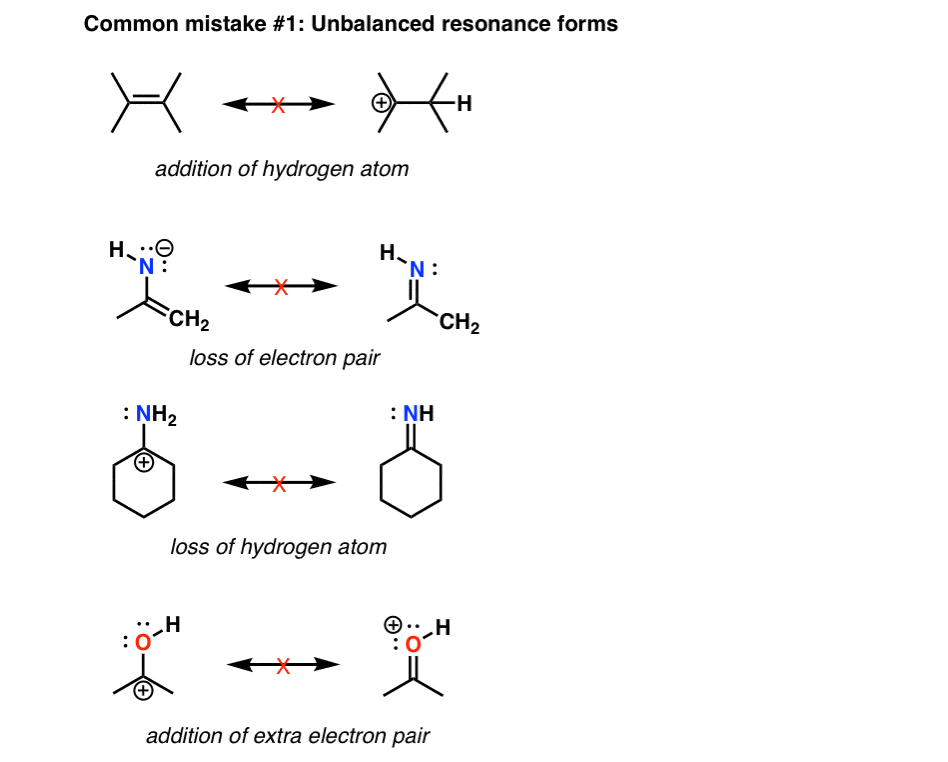
Drawing Resonance Structures 3 Common Mistakes To Avoid
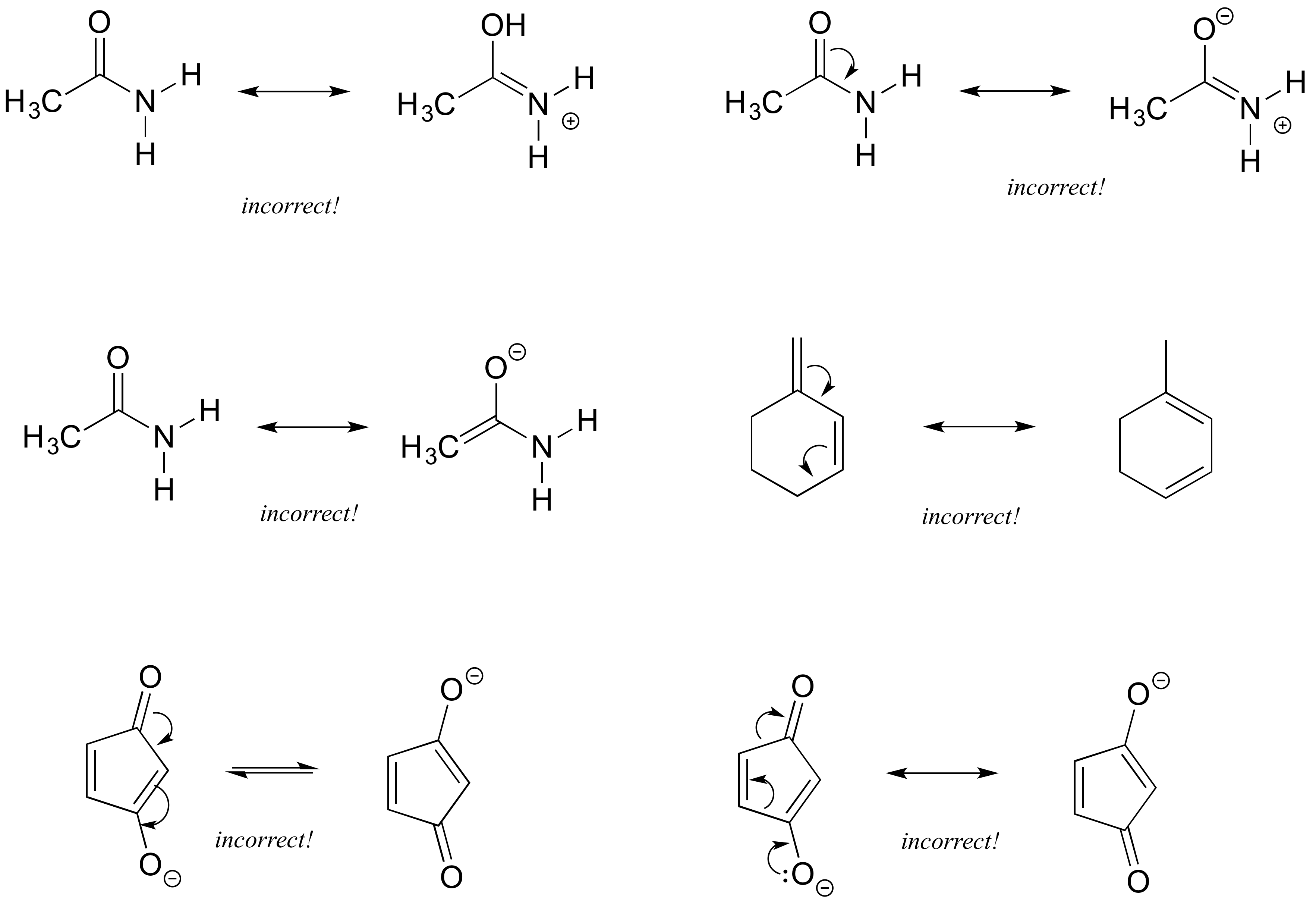
0 comments
Post a Comment